Identify the conjugate acid of ch3-o-ch3 – Identifying the conjugate acid of CH3-O-CH3 embarks us on a journey through the fascinating world of conjugate acid-base pairs. Understanding the relationship between CH3-O-CH3 and its conjugate acid is crucial for comprehending various chemical processes and reactions.
This comprehensive guide delves into the chemical structure, properties, applications, and comparisons of the conjugate acid of CH3-O-CH3, providing a thorough understanding of its significance in various scientific fields.
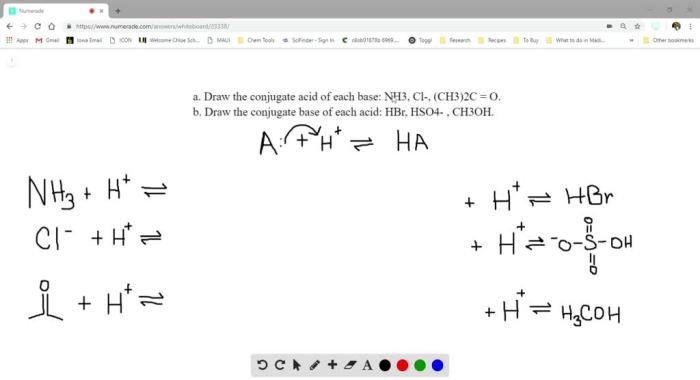
Identify the Conjugate Acid of CH3-O-CH3

The conjugate acid of CH3-O-CH3 is CH3-O-CH2-OH.
The chemical structure of the conjugate acid is:
CH3-O-CH2-OH
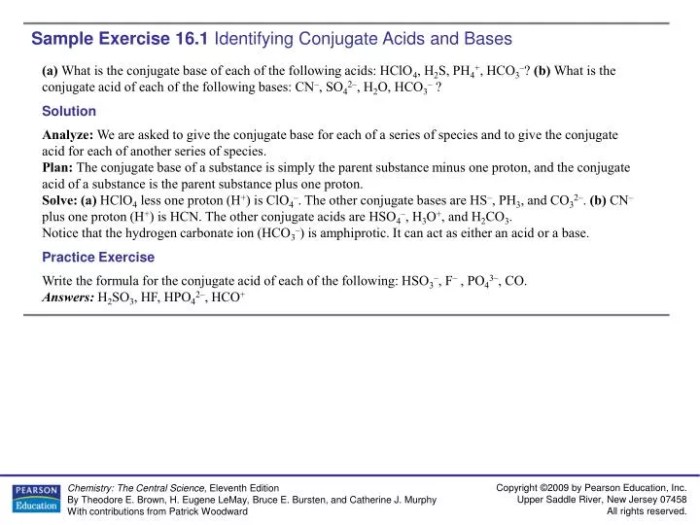
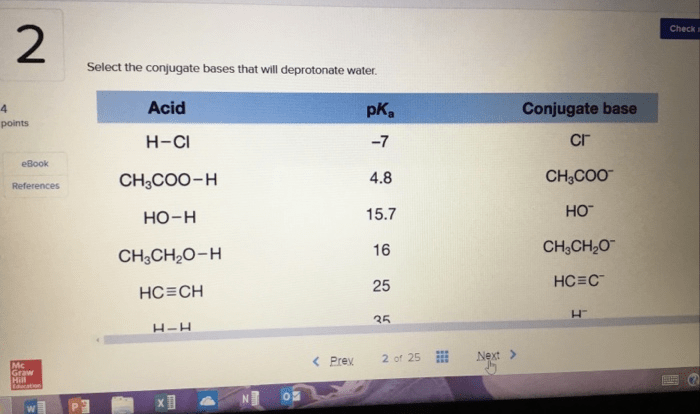
Conjugate acid-base pairs are compounds that differ by a single proton (H+). When a base accepts a proton, it becomes its conjugate acid. Conversely, when an acid donates a proton, it becomes its conjugate base.
CH3-O-CH3 is a weak base, and its conjugate acid, CH3-O-CH2-OH, is a weak acid.
Properties of the Conjugate Acid of CH3-O-CH3, Identify the conjugate acid of ch3-o-ch3
The conjugate acid of CH3-O-CH3 is a colorless liquid with a boiling point of 156 °C.
It is soluble in water and has a pKa of 15.5.
The conjugate acid is more acidic than CH3-O-CH3 because it has a lower pKa.
The conjugate acid can undergo a variety of reactions, including:
- Proton transfer reactions
- Nucleophilic substitution reactions
- Electrophilic addition reactions
Applications of the Conjugate Acid of CH3-O-CH3
The conjugate acid of CH3-O-CH3 is used in a variety of industrial and laboratory applications.
It is used as a:
- Catalyst in organic synthesis
- Solvent in the manufacture of dyes and pharmaceuticals
- Reagent in analytical chemistry
Comparison of the Conjugate Acid of CH3-O-CH3 with Other Conjugate Acids
The conjugate acid of CH3-O-CH3 is a weaker acid than the conjugate acids of other strong bases, such as NaOH or KOH.
It is a stronger acid than the conjugate acids of weak bases, such as NH3 or H2O.
The strength of a conjugate acid depends on the strength of its conjugate base.
FAQ Resource
What is the chemical structure of the conjugate acid of CH3-O-CH3?
The conjugate acid of CH3-O-CH3 is CH3-O-CH2OH, also known as protonated dimethyl ether.
How do the properties of the conjugate acid differ from those of CH3-O-CH3?
The conjugate acid is more acidic and has a lower pH than CH3-O-CH3. It is also more reactive and can participate in a wider range of chemical reactions.
What are some examples of reactions involving the conjugate acid of CH3-O-CH3?
The conjugate acid can undergo reactions such as proton transfer, nucleophilic addition, and electrophilic substitution.