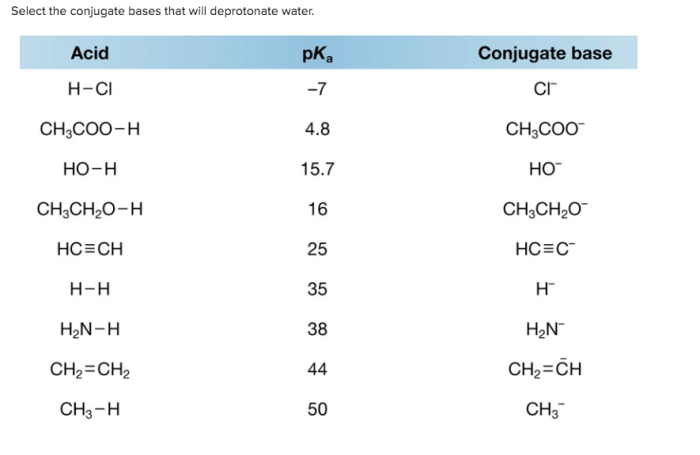
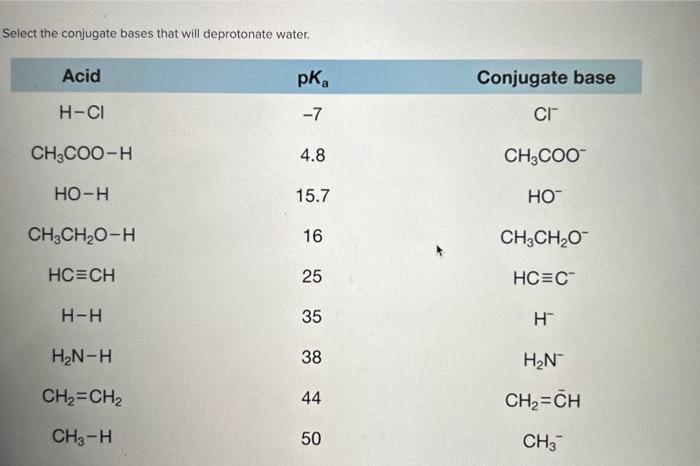
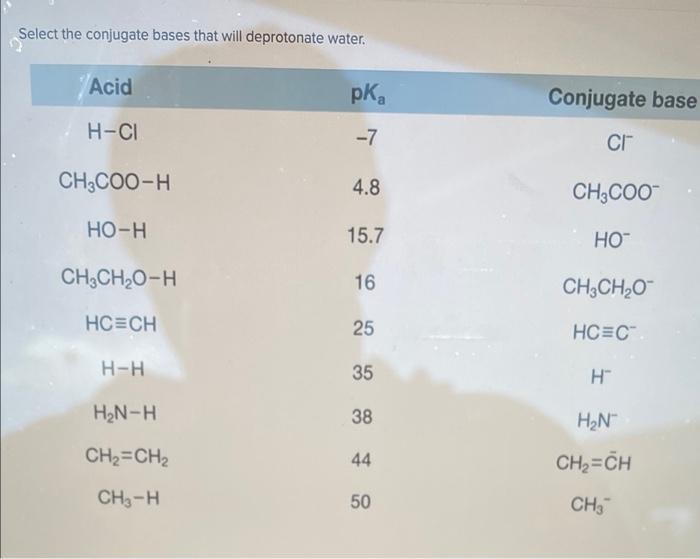
Select the conjugate bases that will deprotonate water – In the realm of chemistry, the concept of conjugate bases plays a crucial role in understanding the behavior of acids and bases. Among the various aspects of conjugate base chemistry, one particularly intriguing topic is the selection of conjugate bases capable of deprotonating water.
This process, known as deprotonation, holds significant implications in various chemical reactions and applications.
Delving into the intricacies of conjugate bases and their ability to deprotonate water, this discussion will explore the fundamental principles, factors influencing deprotonation, and practical applications of this phenomenon. By unraveling the mechanisms and significance of conjugate base-mediated deprotonation, we gain a deeper appreciation for the dynamic nature of chemical reactions and the interplay between acids, bases, and their conjugate counterparts.
Conjugate Bases
A conjugate base is a species that is formed when an acid donates a proton. The conjugate base is the species that remains after the proton has been removed. For example, when hydrochloric acid (HCl) donates a proton, the conjugate base is chloride ion (Cl –). The conjugate acid-base pair is HCl and Cl –.
Deprotonation of Water
Deprotonation is the process of removing a proton from a molecule. Water can be deprotonated by a conjugate base. The conjugate base removes a proton from water, forming hydroxide ion (OH –) and the conjugate acid of the conjugate base.
For example, when sodium hydroxide (NaOH) is added to water, the hydroxide ion deprotonates water, forming OH –and the conjugate acid of NaOH, which is Na +.
Factors Affecting Deprotonation, Select the conjugate bases that will deprotonate water
- The strength of the conjugate base: The stronger the conjugate base, the more easily it can deprotonate water.
- The concentration of the conjugate base: The higher the concentration of the conjugate base, the more likely it is to deprotonate water.
- The temperature: The higher the temperature, the more likely it is for water to be deprotonated.
Applications of Deprotonation
Deprotonation is used in a variety of applications, including:
- Organic synthesis: Deprotonation is used to generate carbanions, which are important intermediates in organic synthesis.
- pH control: Deprotonation is used to control the pH of solutions.
- Analytical chemistry: Deprotonation is used to determine the concentration of acids and bases.
Experimental Techniques
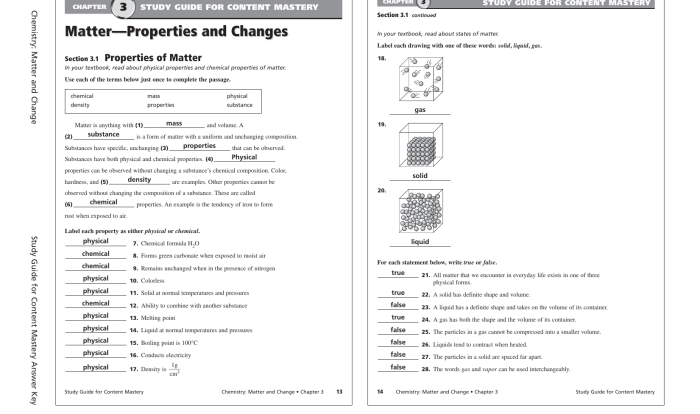
The experimental techniques used to study deprotonation include:
- pH meters: pH meters are used to measure the pH of solutions.
- Titration methods: Titration methods are used to determine the concentration of acids and bases.
- Spectroscopic methods: Spectroscopic methods are used to identify the products of deprotonation reactions.
FAQ Insights: Select The Conjugate Bases That Will Deprotonate Water
What factors influence the ability of a conjugate base to deprotonate water?
The ability of a conjugate base to deprotonate water is influenced by several factors, including its basicity, the strength of the conjugate acid, and the solvent effects.
What are some examples of conjugate bases that can deprotonate water?
Common conjugate bases that can deprotonate water include hydroxide ion (OH-), alkoxide ions (RO-), and amide ions (NH2-).
What are the applications of deprotonation in organic synthesis?
Deprotonation plays a vital role in organic synthesis, enabling the formation of carbon-carbon bonds, the generation of nucleophiles, and the control of reaction mechanisms.