Delving into the realm of geometry, we embark on a captivating exploration of inscribed angles in circles, unraveling their intricate relationship with the circumference of circles. Unit 10 circles homework 5 inscribed angles invites us to uncover the fascinating properties and practical applications of these angles, promising an enlightening journey through the world of mathematical concepts.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of inscribed angles, meticulously defining their unique characteristics and examining their formation within circles. We will unravel the techniques for measuring inscribed angles, unlocking the secrets of the theorem that governs their relationship with intercepted arcs.
Moreover, we will embark on a voyage of discovery, exploring the remarkable properties of inscribed angles, including the intriguing supplementary relationship between opposite inscribed angles. Through interactive diagrams and compelling explanations, we will illuminate these properties, revealing their elegance and mathematical beauty.
Inscribed Angles in Circles
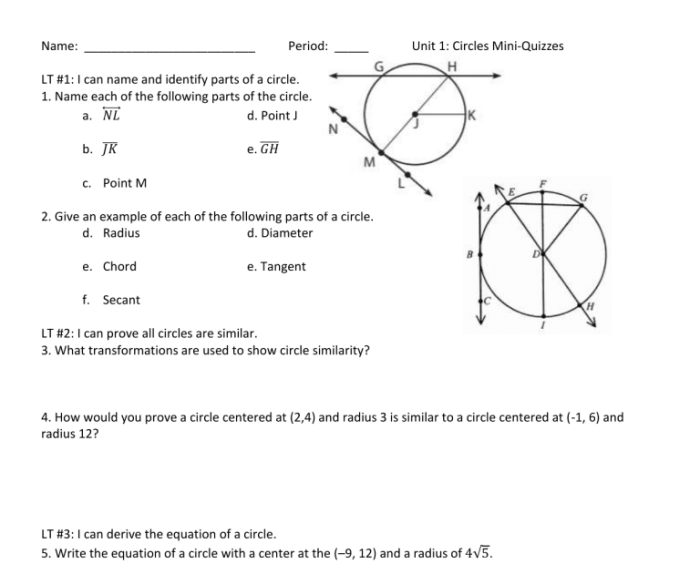
Inscribed angles are angles that are formed by two chords that intersect inside a circle. They are closely related to the circle and its intercepted arcs.
To construct an inscribed angle, simply draw two chords that intersect inside the circle. The angle formed by these chords is an inscribed angle.
Measuring Inscribed Angles, Unit 10 circles homework 5 inscribed angles
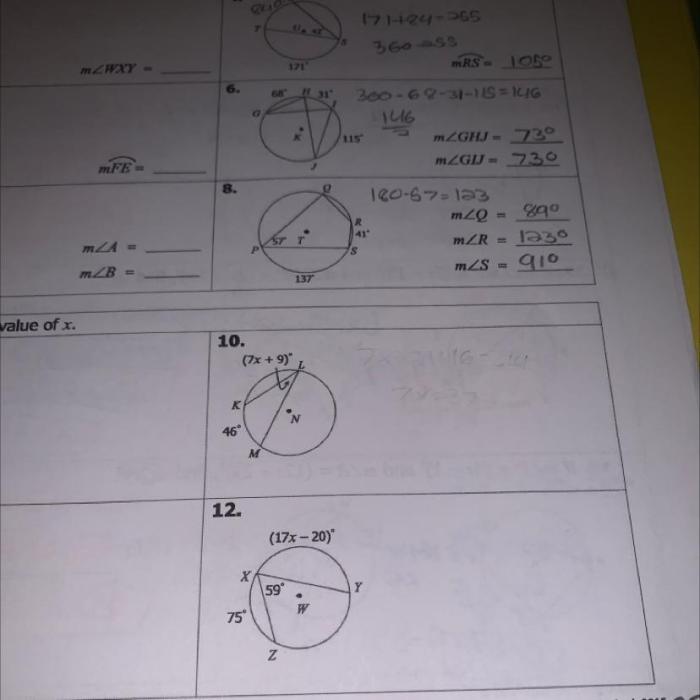
The measure of an inscribed angle is equal to half the measure of its intercepted arc. This means that if an inscribed angle intercepts an arc that measures 120 degrees, then the inscribed angle will measure 60 degrees.
There are a few different methods for measuring inscribed angles. One method is to use a protractor to measure the intercepted arc and then divide that measure by two. Another method is to use the inscribed angle theorem, which states that the measure of an inscribed angle is equal to half the sum of the measures of the two intercepted arcs.
Properties of Inscribed Angles
Inscribed angles have a number of interesting properties. One property is that opposite inscribed angles are supplementary. This means that if two inscribed angles are formed by the same chord, then the sum of their measures will be 180 degrees.
Another property of inscribed angles is that the measure of an inscribed angle is always less than 180 degrees. This is because the intercepted arc must be less than 180 degrees, and the measure of an inscribed angle is half the measure of its intercepted arc.
Applications of Inscribed Angles
Inscribed angles are used in a variety of real-world applications, including architecture and design. For example, inscribed angles can be used to design拱形天花板和圆形窗户.
Commonly Asked Questions: Unit 10 Circles Homework 5 Inscribed Angles
What is an inscribed angle?
An inscribed angle is an angle whose vertex lies on a circle and whose sides intersect the circle.
How do you measure an inscribed angle?
You can measure an inscribed angle by measuring the intercepted arc and then dividing by 2.
What are the properties of inscribed angles?
Inscribed angles have several properties, including the fact that opposite inscribed angles are supplementary.
What are some real-world applications of inscribed angles?
Inscribed angles are used in a variety of real-world applications, such as architecture and design.